Machine Controller
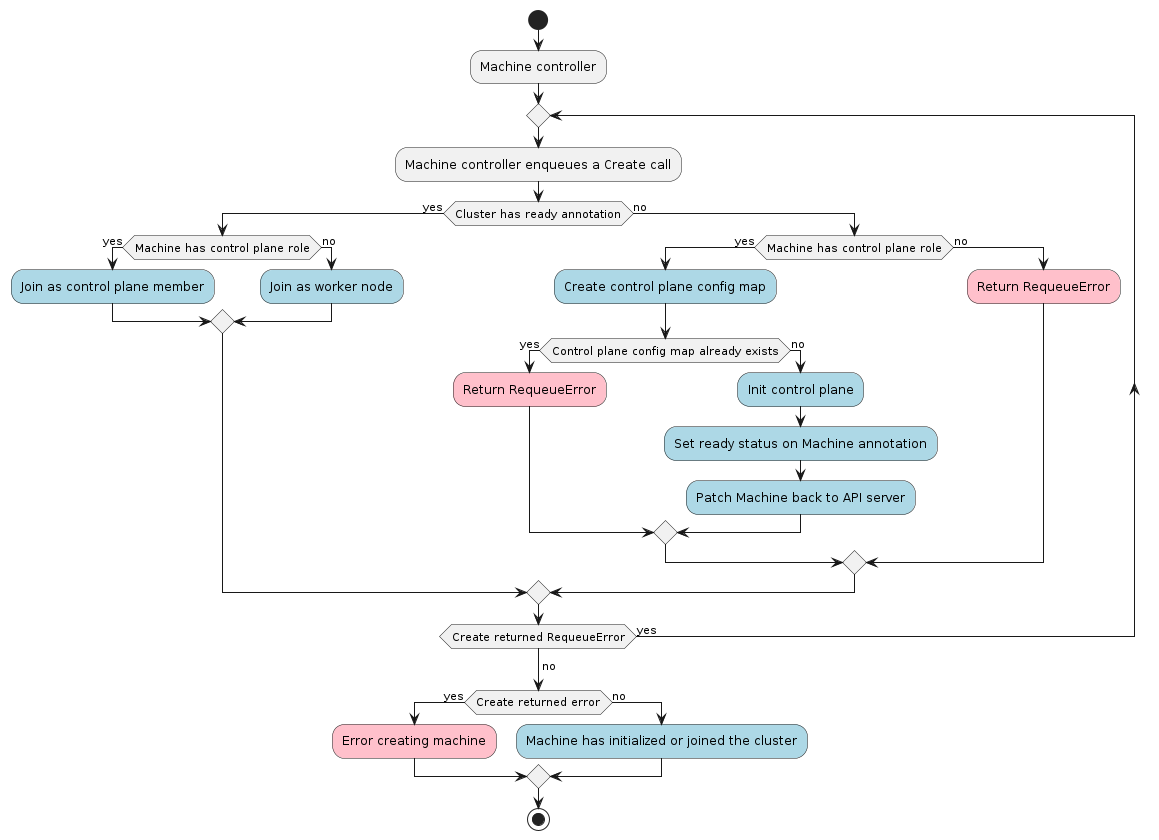
The Machine controller’s main responsibilities are:
- Setting an OwnerReference on:
- Each Machine object to the Cluster object.
- The associated BootstrapConfig object.
- The associated InfrastructureMachine object.
- Copy data from
BootstrapConfig.Status.DataSecretNametoMachine.Spec.Bootstrap.DataSecretNameifMachine.Spec.Bootstrap.DataSecretNameis empty. - Setting NodeRefs to be able to associate machines and Kubernetes nodes.
- Deleting Nodes in the target cluster when the associated machine is deleted.
- Cleanup of related objects.
- Keeping the Machine’s Status object up to date with the InfrastructureMachine’s Status object.
- Finding Kubernetes nodes matching the expected providerID in the workload cluster.
After the machine controller sets the OwnerReferences on the associated objects, it waits for the bootstrap
and infrastructure objects referenced by the machine to have the Status.Ready field set to true. When
the infrastructure object is ready, the machine controller will attempt to read its Spec.ProviderID and
copy it into Machine.Spec.ProviderID.
The machine controller uses the kubeconfig for the new workload cluster to watch new nodes coming up.
When a node appears with Node.Spec.ProviderID matching Machine.Spec.ProviderID, the machine controller
transitions the associated machine into the Provisioned state. When the infrastructure ref is also
Ready, the machine controller marks the machine as Running.
Contracts
Cluster API
Cluster associations are made via labels.
Expected labels
| what | label | value | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine | cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name | <cluster-name> | Identify a machine as belonging to a cluster with the name <cluster-name> |
| Machine | cluster.x-k8s.io/control-plane | true | Identifies a machine as a control-plane node |
Bootstrap provider
The BootstrapConfig object must have a status object.
To override the bootstrap provider, a user (or external system) can directly set the Machine.Spec.Bootstrap.Data
field. This will mark the machine as ready for bootstrapping and no bootstrap data will be copied from the
BootstrapConfig object.
Required status fields
The status object must have several fields defined:
ready- a boolean field indicating the bootstrap config data is generated and ready for use.dataSecretName- a string field referencing the name of the secret that stores the generated bootstrap data.
Optional status fields
The status object may define several fields that do not affect functionality if missing:
failureReason- a string field explaining why a fatal error has occurred, if possible.failureMessage- a string field that holds the message contained by the error.
Note: once any of failureReason or failureMessage surface on the machine who is referencing the bootstrap config object,
they cannot be restored anymore (it is considered a terminal error; the only way to recover is to delete and recreate the machine).
Also, if the machine is under control of a MachineHealthCheck instance, the machine will be automatically remediated.
Example:
kind: MyBootstrapProviderConfig
apiVersion: bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
status:
ready: true
dataSecretName: "MyBootstrapSecret"
Infrastructure provider
The InfrastructureMachine object must have both spec and status objects.
Required spec fields
The spec object must at least one field defined:
providerID- a cloud provider ID identifying the machine.
Optional spec fields
The spec object may define several fields that do not affect functionality if missing:
failureDomain- is a string identifying the failure domain the instance is running in.
Required status fields
The status object must at least one field defined:
ready- a boolean field indicating if the infrastructure is ready to be used or not.
Optional status fields
The status object may define several fields that do not affect functionality if missing:
failureReason- is a string that explains why a fatal error has occurred, if possible.failureMessage- is a string that holds the message contained by the error.addresses- is aMachineAddresses(a list ofMachineAddress) which represents host names, external IP addresses, internal IP addresses, external DNS names, and/or internal DNS names for the provider’s machine instance.MachineAddressis defined as:type(string): one ofHostname,ExternalIP,InternalIP,ExternalDNS,InternalDNSaddress(string)
Note: once any of failureReason or failureMessage surface on the machine who is referencing the infrastructureMachine object,
they cannot be restored anymore (it is considered a terminal error; the only way to recover is to delete and recreate the machine).
Also, if the machine is under control of a MachineHealthCheck instance, the machine will be automatically remediated.
Example:
kind: MyMachine
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
spec:
providerID: cloud:////my-cloud-provider-id
status:
ready: true
Secrets
The Machine controller will create a secret or use an existing secret in the following format:
| secret name | field name | content |
|---|---|---|
<cluster-name>-kubeconfig | value | base64 encoded kubeconfig that is authenticated with the child cluster |