MachinePool Controller
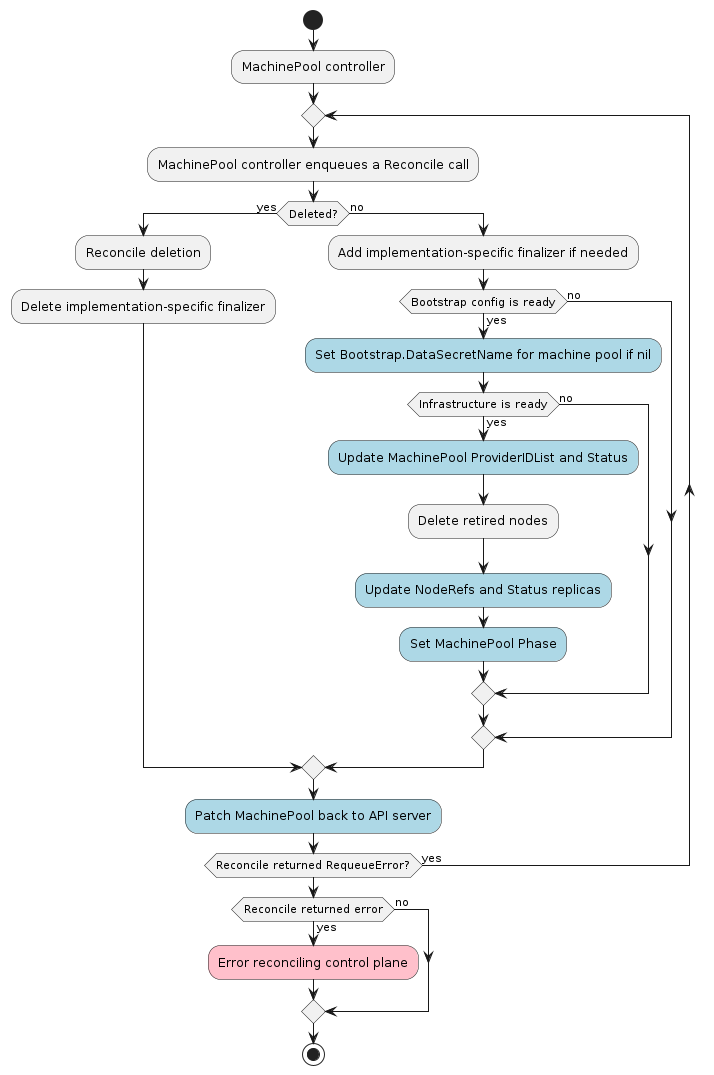
The MachinePool controller’s main responsibilities are:
- Setting an OwnerReference on each MachinePool object to:
- The associated Cluster object.
- The associated BootstrapConfig object.
- The associated InfrastructureMachinePool object.
- Copy data from
BootstrapConfig.Status.DataSecretNametoMachinePool.Spec.Template.Spec.Bootstrap.DataSecretNameifMachinePool.Spec.Template.Spec.Bootstrap.DataSecretNameis empty. - Setting NodeRefs on MachinePool instances to be able to associate them with Kubernetes nodes.
- Deleting Nodes in the target cluster when the associated MachinePool instance is deleted.
- Keeping the MachinePool’s Status object up to date with the InfrastructureMachinePool’s Status object.
- Finding Kubernetes nodes matching the expected providerIDs in the workload cluster.
After the machine pool controller sets the OwnerReferences on the associated objects, it waits for the bootstrap
and infrastructure objects referenced by the machine to have the Status.Ready field set to true. When
the infrastructure object is ready, the machine pool controller will attempt to read its Spec.ProviderIDList and
copy it into MachinePool.Spec.ProviderIDList.
The machine pool controller uses the kubeconfig for the new workload cluster to watch new nodes coming up.
When a node appears with a Node.Spec.ProviderID in MachinePool.Spec.ProviderIDList, the machine pool controller
increments the number of ready replicas. When all replicas are ready and the infrastructure ref is also
Ready, the machine pool controller marks the machine pool as Running.
Contracts
Cluster API
Cluster associations are made via labels.
Expected labels
| what | label | value | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| MachinePool | cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name | <cluster-name> | Identify a machine pool as belonging to a cluster with the name <cluster-name> |
Bootstrap provider
The BootstrapConfig object must have a status object.
The CRD name must have the format produced by sigs.k8s.io/cluster-api/util/contract.CalculateCRDName(Group, Kind).
To override the bootstrap provider, a user (or external system) can directly set the MachinePool.Spec.Bootstrap.DataSecretName
field. This will mark the machine as ready for bootstrapping and no bootstrap data secret name will be copied from the
BootstrapConfig object.
Required status fields
The status object must have several fields defined:
ready- a boolean field indicating the bootstrap config data is generated and ready for use.dataSecretName- a string field referencing the name of the secret that stores the generated bootstrap data.
Optional status fields
The status object may define several fields that do not affect functionality if missing:
failureReason- a string field explaining why a fatal error has occurred, if possible.failureMessage- a string field that holds the message contained by the error.
Note: once any of failureReason or failureMessage surface on the machine pool who is referencing the bootstrap config object,
they cannot be restored anymore (it is considered a terminal error; the only way to recover is to delete and recreate the machine pool).
Example:
kind: MyBootstrapProviderConfig
apiVersion: bootstrap.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
status:
ready: true
dataSecretName: "MyBootstrapSecret"
Infrastructure provider
The InfrastructureMachinePool object must have both spec and status objects.
The CRD name must have the format produced by sigs.k8s.io/cluster-api/util/contract.CalculateCRDName(Group, Kind).
Required spec fields
The spec object must have at least one field defined:
providerIDList- the list of cloud provider IDs identifying the instances.
Required status fields
The status object must have at least one field defined:
ready- a boolean field indicating if the infrastructure is ready to be used or not.
Optional status fields
The status object may define several fields that do not affect functionality if missing:
failureReason- is a string that explains why a fatal error has occurred, if possible.failureMessage- is a string that holds the message contained by the error.infrastructureMachineKind- the kind of the InfraMachines. This should be set if the InfrastructureMachinePool plans to support MachinePool Machines.
Note: once any of failureReason or failureMessage surface on the machine pool who is referencing the InfrastructureMachinePool object,
they cannot be restored anymore (it is considered a terminal error; the only way to recover is to delete and recreate the machine pool).
Note: Infrastructure providers can support MachinePool Machines by having the InfraMachinePool set the infrastructureMachineKind to the kind of their InfrastructureMachines. The InfrastructureMachinePool will be responsible for creating InfrastructureMachines as the MachinePool is scaled up, and the MachinePool controller will create Machines for each InfrastructureMachine and set the ownerRef. The InfrastructureMachinePool will be responsible for deleting the Machines as the MachinePool is scaled down in order for the Machine deletion workflow to function properly. In addition, the InfrastructureMachines must also have the following labels set by the InfrastructureMachinePool: cluster.x-k8s.io/cluster-name and cluster.x-k8s.io/pool-name. The MachinePoolNameLabel must also be formatted with capilabels.MustFormatValue() so that it will not exceed character limits.
Example
kind: MyMachinePool
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1beta1
spec:
providerIDList:
- cloud:////my-cloud-provider-id-0
- cloud:////my-cloud-provider-id-1
status:
ready: true
infrastructureMachineKind: InfrastructureMachine
Externally Managed Autoscaler
A provider may implement an InfrastructureMachinePool that is externally managed by an autoscaler. For example, if you are using a Managed Kubernetes provider, it may include its own autoscaler solution. To indicate this to Cluster API, you would decorate the MachinePool object with the following annotation:
"cluster.x-k8s.io/replicas-managed-by": ""
Cluster API treats the annotation as a “boolean”, meaning that the presence of the annotation is sufficient to indicate external replica count management, with one exception: if the value is "false", then that indicates to Cluster API that replica enforcement is nominal, and managed by Cluster API.
Providers may choose to implement the cluster.x-k8s.io/replicas-managed-by annotation with different values (e.g., external-autoscaler, or karpenter) that may inform different provider-specific behaviors, but those values will have no effect upon Cluster API.
The effect upon Cluster API of this annotation is that during autoscaling events (initiated externally, not by Cluster API), when more or fewer MachinePool replicas are observed compared to the Spec.Replicas configuration, it will update its Status.Phase property to the value of "Scaling".
Example:
kind: MyMachinePool
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha3
spec:
providerIDList:
- cloud:////my-cloud-provider-id-0
- cloud:////my-cloud-provider-id-1
- cloud:////my-cloud-provider-id-2
replicas: 1
status:
ready: true
phase: Scaling
infrastructureMachineKind: InfrastructureMachine
It is the provider’s responsibility to update Cluster API’s Spec.Replicas property to the value observed in the underlying infra environment as it changes in response to external autoscaling behaviors. Once that is done, and the number of providerID items is equal to the Spec.Replicas property, the MachinePools’s Status.Phase property will be set to Running by Cluster API.
Secrets
The machine pool controller will use a secret in the following format:
| secret name | field name | content |
|---|---|---|
<cluster-name>-kubeconfig | value | base64 encoded kubeconfig that is authenticated with the workload cluster |